21 febbraio 2023
Sulla rivista scientifica Scientia Horticulturae è appena uscito un nuovo articolo scientifico dal titolo “Crescita, qualità nutrizionali e capacità antiossidante della lattuga coltivata su due diversi terreni con fertilizzanti a base di zolfo, organici e chimici”. L’articolo è stato scritto dal nostro partner di progetto, Prof. Muscolo, in collaborazione con alcuni dei suoi colleghi dell’Università Mediterranea; il lavoro svolto nel progetto LIFE RecOrgFert PLUS è stato riconosciuto.
Scientia Horticulturae è una rivista internazionale che pubblica ricerche relative alle colture orticole. Gli articoli sulla rivista trattano della produzione aperta o protetta di ortaggi, frutta, funghi commestibili e piante ornamentali in condizioni temperate, subtropicali e tropicali. Gli articoli in aree correlate (biochimica, micropropagazione, scienze del suolo, selezione vegetale, fisiologia vegetale, fitopatologia, ecc.) sono presi in considerazione, se contengono informazioni di diretto significato per l’orticoltura.
Qui sotto è presente l’abstract dell’articolo:
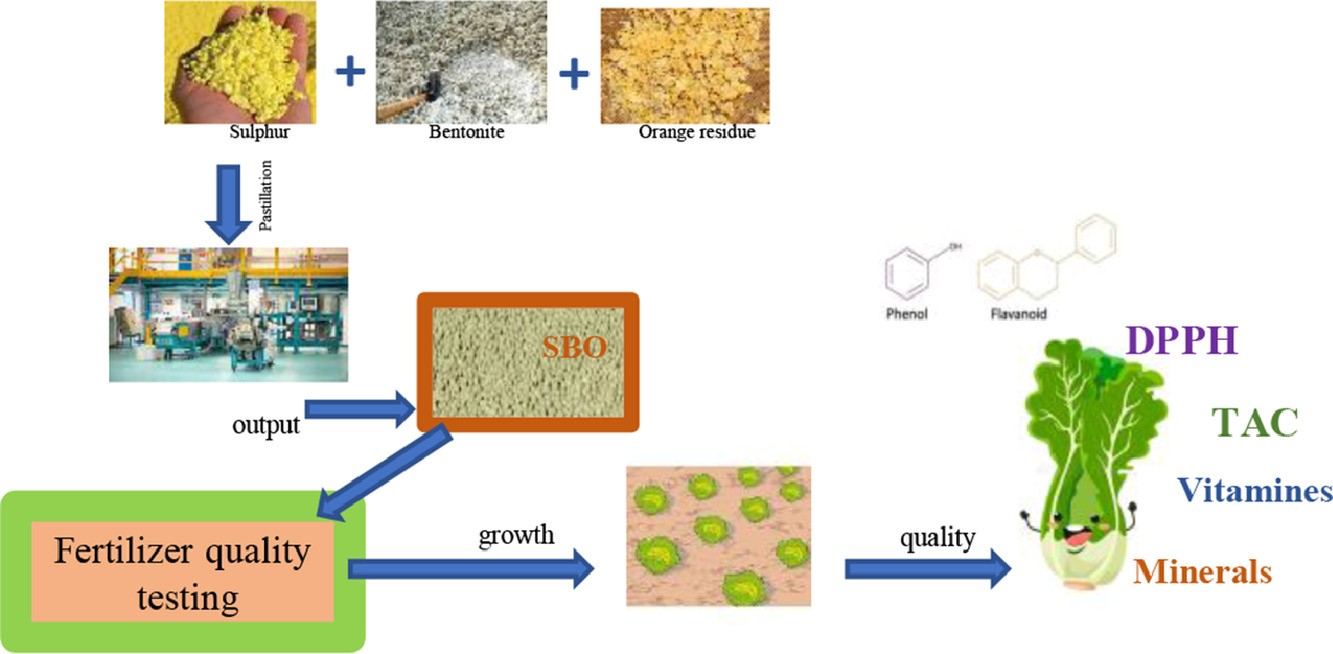
Organic and industrial wastes represent a great opportunity to produce organic-mineral fertilizers for land restoration and crop quality improvement. The principal interest of this work was to use sulphur recovered from the residues of hydrocarbon refining processes, and orange wastes from food industry processing stabilized with bentonite (SBO) to cultivate lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.), one of the most produced green leafy vegetable worldwide. The aim of the present study was to cultivate lettuce in open field, in two different soils, using the mineral-organic fertilizer (SBO) at different concentrations, in comparison to chemical fertilizer (NPK), horse manure (HM) and to a control (unfertilized soil). The impact of the new fertilizer on lettuce growth and quality (nutrients and antioxidants) was investigated. Results evidenced that sulphur-based-fertilizer increased mainly the quality rather than the growth of lettuce independently from the soil characteristics. The fertilization with SBO increased the amount of potassium and sulphate in lettuce grown in both soils in respect to fertilizer concentration. In both locations, a stimulatory effect of SBO fertilizer, more on secondary metabolites than primary metabolites, in particular flavonoids, phenols, vitamins C and E, was observed. The antioxidant activities expressed as DPPH and TAC, also increased in lettuce grown with SBO at all concentrations compared to CTR and the other treatments, the increase was dependant on the SBO concentration. In short, lettuce was found enriched of anti-inflammatory compounds and vitamins when cultivated with SBO. The highest antioxidant activities, in SBO grown lettuce, were correlated to the high amount of phenols for DPPH, and flavonoids, vitamin C and E for TAC. These results can be useful for both nutraceutical and agronomic purposes.
Curioso di leggere l’intero articolo? Leggilo QUI >>




